By Munira Iqbal
World Hunger
Discover the causes of world hunger and learn about efforts to combat this pressing issue. Explore the impact of poverty, conflict, and climate change on global food security. Find out how sustainable agriculture and collaborative initiatives can make a difference.
Introduction
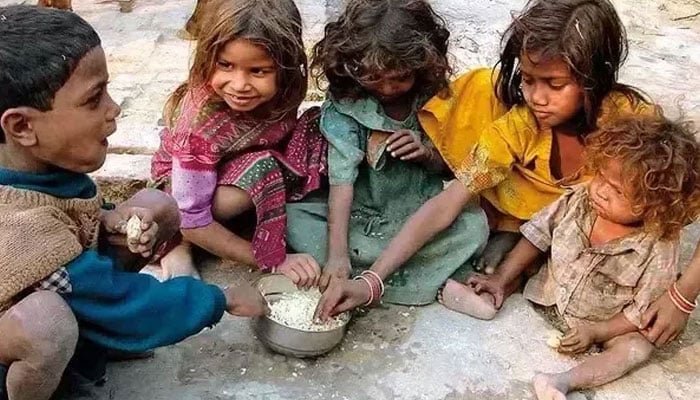
In a world abundant with resources and technological advancements, it’s disheartening to acknowledge the persisting crisis of world hunger. After a decade of steady decline, the issue of global hunger is resurfacing, affecting nearly 10% of the global population. From 2019 to 2022, the number of undernourished individuals increased by a staggering 150 million. This growing crisis is driven primarily by conflicts, climate change, and the unforeseen impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Definition of World Hunger
World hunger refers to the widespread and chronic lack of sufficient food and proper nutrition among a significant portion of the global population. It is a pressing issue that arises when people, often in impoverished regions, do not have access to an adequate amount of nutritious food to meet their daily dietary needs. This condition can lead to malnutrition, weakened immune systems, stunted growth, and even death.
World hunger is driven by various factors including poverty, inequality, conflict, climate change, and lack of access to education and healthcare. Addressing world hunger requires comprehensive strategies that tackle its root causes and promote sustainable development and equitable resource distribution.
The Alarming Numbers
As of 2023, the Global Hunger Index paints a sobering picture of the situation. Despite the abundance of food produced worldwide, a shocking 783 million people continue to experience hunger daily. This statistic serves as a stark reminder that adequate nourishment remains elusive for a significant portion of the world’s population.
1. 14 Million Children Suffer from Severe Acute Malnutrition
The innocence of childhood is marred by the harsh reality that 14 million children are grappling with severe acute malnutrition. This condition not only threatens their physical development but also hinders their ability to lead a healthy and prosperous life.
2. 45% of Child Deaths Worldwide Are Due to Hunger & Related Causes
Tragically, almost half of child deaths across the globe are attributed to hunger and its related consequences. These young lives are cut short due to a lack of access to basic nutrition, showcasing the urgent need for global action.
3. 700 Children Die Each Day from Illnesses Caused by Dirty Water and Unhygienic Living Conditions
Beyond the direct effects of hunger, unclean water and unsanitary living conditions pose significant threats to the vulnerable. Every single day, 700 children succumb to illnesses stemming from these dire circumstances.
Causes of World Hunger
The causes of world hunger are multifaceted and complex, often stemming from a combination of social, economic, political, and environmental factors. Some of the key causes of world hunger include:
- Poverty: A lack of income and resources prevents many individuals and families from accessing sufficient food. Poverty limits people’s ability to purchase or produce the food they need to meet their nutritional requirements.
- Inequality: Disparities in income distribution and access to resources contribute to hunger. Marginalized and vulnerable populations often have limited access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities, worsening food insecurity.
- Conflict and Violence: Armed conflicts, wars, and political instability disrupt agricultural production, displace communities, and hinder food distribution systems. This can lead to food shortages and limited access to basic necessities.
- Climate Change: Changing weather patterns, extreme weather events, and environmental degradation impact agricultural productivity. Crop failures, water scarcity, and disrupted ecosystems can lead to food shortages.
- Lack of Access to Education: Lack of education can limit people’s ability to adopt sustainable farming practices, make informed dietary choices, and access information about nutrition.
- Limited Access to Healthcare: Poor health and limited access to healthcare can lead to malnutrition and reduced productivity, perpetuating the cycle of poverty and hunger.
- Unstable Markets: Fluctuations in food prices and market volatility can impact affordability and access to food, especially for vulnerable populations.
- Gender Inequality: Women often face limited access to resources, land, and credit, which can restrain their ability to produce and access food for themselves and their families.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Insufficient transportation, storage, and distribution systems can result in food wastage and difficulties in getting food to those who need it.
- Political Instability: Poor governance, corruption, and lack of effective policies can impede agricultural development and hinder food distribution systems.
- Land Degradation: Soil erosion, deforestation, and land degradation reduce the productivity of agricultural land, making it harder to produce enough food.
- Population Growth: Rapid population growth can outpace the growth of food production, straining resources and exacerbating food scarcity.
- Lack of Investment: Insufficient investment in agricultural infrastructure, technology, and research can hinder agricultural productivity and food security.
- Global Trade Policies: Unfavorable trade policies can disadvantage developing countries in the global market, affecting their ability to import and export food.
- Food Waste: High levels of food waste and loss in both production and consumption contribute to food scarcity.
Addressing world hunger requires comprehensive strategies that tackle these interconnected causes and promote sustainable development, equitable access to resources, and social justice
Link Sustainable Development
Addressing the Crisis
The path to combating the global hunger crisis is challenging, but there are promising avenues that deserve exploration. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) emphasizes the need to reduce the costs of nutritious foods and ensure the affordability of healthy diets for everyone. Achieving this goal requires substantial transformations within existing food systems on a global scale.
1. Transforming Food Systems
International trade barriers and rising tariffs must be lowered to ensure widespread access to nutritious foods. Additionally, agricultural policies should shift towards a more nutrition-sensitive approach, with increased support for fruit and vegetable crops. Government policies play a pivotal role in this transformation, encompassing measures such as altering the taxation of energy-dense foods, improving the regulation of food industries, and implementing policies to promote nutrition education.
2. The Opportunity Amidst the Challenges
While the challenges are significant, the FAO highlights the presence of substantial opportunities to alleviate the global hunger crisis. Through collaborative efforts on governmental, organizational, and individual levels, progress can be made towards a world where hunger is a thing of the past.
3. 4 Ways Countries Are Successfully Fighting Hunger
The article, published by the World Economic Forum on September 17, 2015, delves into the complex issue of sustainable development and its intersections with global hunger. The piece focuses on Goal 2 of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): “End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture.” The author emphasizes the need for practical solutions that address the multifaceted challenges of sustainable development and highlights the role of sustainable agriculture as a cross-cutting strategy.
The author (Bruce Campbell serves as the director of the Climate Change, Agriculture, and Food Security research program, a strategic partnership between CGIAR and Future Earth.) acknowledges the complexity of the 17 SDGs and their related 169 targets, expressing concerns about whether such ambitious goals can realistically be achieved. The tendency to compartmentalize issues and treat them in isolation is critiqued as counterproductive. The central question raised is how to navigate this complexity while identifying practical interventions that drives sustainable development.
Sustainable agriculture is presented as a pivotal solution that intersects with multiple SDGs. Notably, it aligns with poverty eradication (SDG1), water management (SDG6), economic growth (SDG8), climate action (SDG13), and more. The concept of climate-smart agriculture, which addresses climate change adaptation and reducing agriculture’s carbon footprint, is introduced as a powerful tool to combat climate-related threats to food security.
The article then highlights four countries that are successfully implementing climate-smart agricultural practices to target various SDGs:
- India: The National Food Security Act aims to provide access to subsidized food for 800 million people. By distributing nutritious coarse grains alongside staples like rice and wheat, India seeks to enhance climate adaptation and food security. This initiative benefits both farmers and vulnerable populations.
- Kenya: The World Agroforestry Centre assists farmers in producing more milk with fewer emissions through improved livestock feeding practices. Scaling up these climate-smart actions can significantly reduce emissions, create jobs, and improve livelihoods.
- Colombia: To combat extreme climate events affecting crops, Colombia engaged in a knowledge exchange with Senegal, developing localized climate information for farmers’ planning systems. By sharing climate advice, the project enhances farmers’ decision-making and empowers women.
- Nigeria: Nigeria aims to insure smallholder farmers against extreme weather events. Collaborations with research institutes are formulating comprehensive strategies to ensure nationwide coverage, helping farmers recover from climate-related disasters.
The article concludes by urging countries and investors to recognize the potential of financing agricultural research and development to yield comprehensive, cross-cutting solutions that contribute to multiple SDGs. It underscores the importance of collaboration with farmers to achieve lasting solutions and underscores the power of climate-smart agriculture in addressing the world’s most pressing challenges.
Pakistan is Introducing Corporate Farming
Pakistan is thinking about doing corporate farming. People are worried it might hurt fertile landowners and small farmers. This could make the country’s food security problem worse. The government’s policies aren’t strong enough, and they don’t always do what they promise. Also, there’s a lot of problems with the government being unstable and not always honest. This makes the food security situation worse and makes people question if corporate farming is a good idea. But, if corporate farming works together with local farmers, it could help Pakistan with its food problems. (You can read the details here.)
Conclusion
The persistent crisis of world hunger continues to cast a shadow over a world rich in resources and technological advancements. Despite a decade of progress, global hunger is on the rise again, affecting almost 10% of the world’s population. The surge in undernourished individuals, the alarming statistics, and the heartbreaking facts of child malnutrition and related deaths underscore the urgent need for comprehensive action. The causes of world hunger are intricate and interconnected, stemming from poverty, inequality, conflict, climate change, lack of education and healthcare, and more. Addressing this crisis requires a holistic approach that encompasses sustainable development, equitable resource distribution, and social justice.

Check out our monthly English and Urdu magazines on Homepage
FAQs:
- What are the main causes of world hunger? World hunger is caused by a combination of factors, including poverty, inequality, conflict, climate change, lack of education and healthcare, unstable markets, gender inequality, and more.
- What percentage of the global population experiences hunger daily? Nearly 10% of the global population continues to face hunger on a daily basis.
- How has global hunger been affected by conflicts and climate change? Armed conflicts and climate change disrupt agricultural production, displace communities, and hinder food distribution systems, leading to food shortages and insecurity.
- What are some of the alarming consequences of child malnutrition? Child malnutrition not only hampers physical development; but also chokes the path to a healthy and prosperous life for millions of children. Almost 45% of child deaths globally are attributed to hunger-related causes.
- What strategies can help address the global hunger crisis? To combat global hunger, comprehensive strategies are needed, including reducing the costs of nutritious foods, ensuring access to healthy diets, shifting towards nutrition-sensitive agriculture, and implementing policies that support nutrition education and equitable resource distribution.
- How does climate-smart agriculture contribute to addressing hunger? Climate-smart agriculture, which focuses on climate change adaptation and reducing the carbon footprint of agriculture, can enhance food security, create jobs, and contribute to economic growth while addressing climate-related threats to food supply.
- What are some successful approaches that countries are using to fight hunger? Countries like India, Kenya, Colombia, and Nigeria are implementing climate-smart agricultural practices, distributing nutritious foods, improving livestock feeding practices, and providing weather insurance for farmers to combat hunger and promote sustainable development.
- Why is collaboration with farmers important in addressing hunger? Collaborating with farmers is crucial for designing and implementing effective solutions as they play a key role in food production. Their insights and involvement ensure that interventions are practical, sustainable, and planned to local contexts.
- How does addressing hunger contribute to achieving multiple Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)? Strategies to combat hunger often intersect with various SDGs, including poverty eradication, water management, economic growth, climate action, gender equality, and more, highlighting the interconnected nature of global challenges.
- What is the ultimate goal in addressing global hunger? The ultimate goal in addressing global hunger is to create a world where every individual has access to sufficient, nutritious food, and where social, economic, and environmental factors are in harmony to ensure a sustainable and just future for all.
Subscribe our website for latest updates:
https://republicpolicy.com/shop/
Read More