Zafar Iqbal
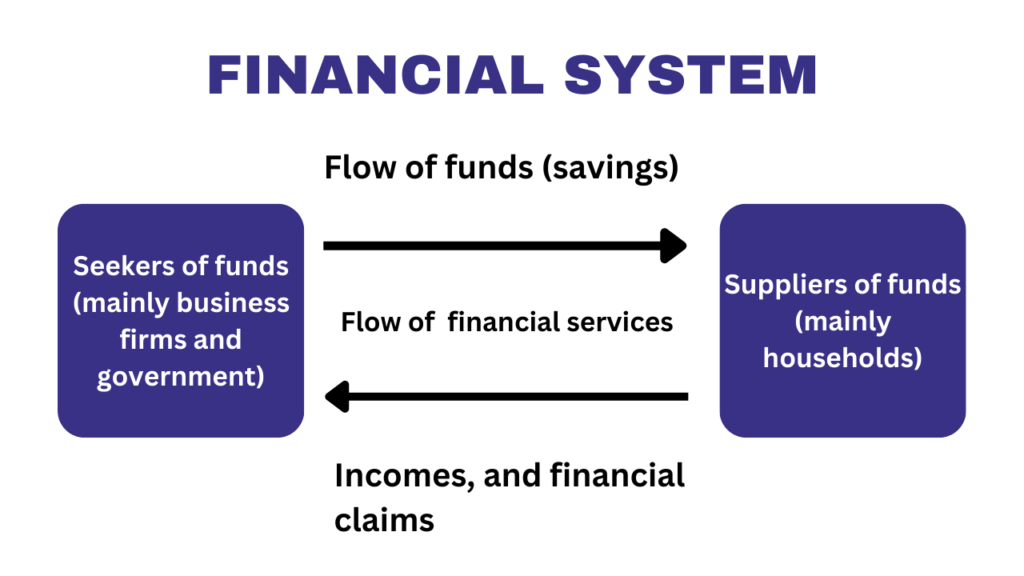
A robust financial system comprising dynamic capital markets and a strong banking sector is widely recognized as a critical driver of investment, productivity, and sustainable economic growth. In this discussion, we delve into the substantial impact of well-developed financial systems on the economies of the United States (US), India, and Pakistan.
The United States, as the largest and most developed market, stands as a beacon of success in leveraging its financial system to drive economic growth. With a market capitalization of over $50 trillion, equivalent to approximately 170 per cent of its GDP, the US boasts the largest and most liquid capital market in the world. This vast market has enabled companies to raise substantial funds through equity and debt offerings, fueling business expansion and innovation across various industries.
In contrast, the emerging market economy of India has also witnessed remarkable growth in its capital markets, making it one of the fastest-growing economies. With a market capitalization of around $5 trillion, approximately 128 per cent of the country’s GDP, India’s stock market has been instrumental in raising capital for key sectors such as technology, infrastructure, manufacturing, and consumer goods. The expansion of India’s capital market, coupled with a surge in venture capital and private equity, has significantly contributed to the country’s economic development and the emergence of successful corporations and startups.
However, Pakistan’s financial systems, particularly its capital market and banking sector, have remained underdeveloped, leading to an underperforming economy struggling with low productivity and a recurring need for international bailouts. Despite recent upsurges, the market capitalization of the Pakistan Stock Exchange (PSX) remains significantly lower compared to its counterparts. This underdevelopment has hindered the country’s ability to finance expansion and invest in innovation, contributing to its stagnant economy.
Moving beyond the capital markets, the banking sectors of the US and India have played crucial roles in supporting economic growth. American banks hold total assets of over $23 trillion, actively channeling deposits into productive lending for businesses and households, thereby driving economic activity. Similarly, India’s banking sector, with around 85 per cent of total banking assets and deposits of about 80 per cent of GDP, has significantly contributed to financing public and private sector initiatives, supporting infrastructure development, corporates, small businesses, and entrepreneurship.
Conversely, Pakistan’s banking sector presents a bleaker picture, with a low advances-to-deposit ratio, indicating a lack of productive lending to the private sector. The significant portion of deposits being invested in government securities has starved the private sector of necessary credit, limiting its ability to invest in new technologies, expand production, and create jobs. This trend has stifled Pakistan’s economic progress, leaving it struggling to keep pace with global economic developments and trends.
In conclusion, the experiences of the US, India, and Pakistan highlight the profound impact of robust financial systems on economic growth. While the US and India have leveraged their financial systems to drive innovation, productivity, and sustained economic growth, Pakistan’s underdeveloped financial infrastructure has hindered its economic progress, leaving its private sector starved of necessary capital. Without significant reforms to its banking sector and capital markets, Pakistan risks continuing down the path of stagnation and indebtedness, emphasizing the critical role of robust financial infrastructure in fostering sustainable economic growth and development.