By: Dr Arsalan Nazir
The general Cadre Bureaucracy is unspecialized bureaucracy & often remains incompetent to solve & lead technical- specialized operation. The worst part is their incapability to solve public financial & developmental operations. Hence, PFM is the worst performance area of general Cadre Bureaucracy in Pakistan.
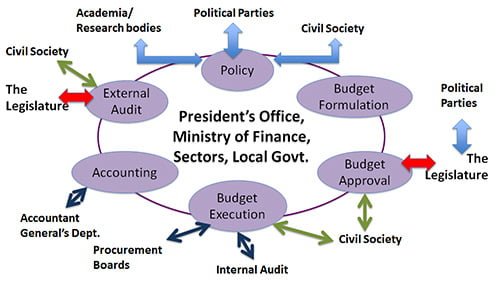
Public financial management (PFM) refers to the set of processes and systems that governments use to manage public resources, including budgeting, accounting, financial reporting, and auditing. Effective PFM is critical for ensuring transparency, accountability, and good governance, as well as for promoting economic growth and development.
There are several different kinds of PFM, including:
- Budgeting: This involves the process of preparing and executing a government’s budget, including revenue collection, resource allocation, and expenditure planning.
- Accounting and financial reporting: This involves the recording of financial transactions and the preparation of financial statements, such as balance sheets and income statements.
- Auditing: This involves the independent examination of financial statements to ensure their accuracy and compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
- Fiscal decentralization: This involves the transfer of fiscal responsibilities from the central government to subnational governments, such as provinces or municipalities.
- Public debt management: This involves the management of government borrowing and debt repayment, including the issuance of bonds and other financial instruments.
In Pakistan, there are several capacity crises facing PFM, including a lack of skilled personnel, inadequate systems and processes, and weak institutional frameworks. To enhance the capacity of public finance managers in Pakistan, several strategies could be adopted, including:
- Strengthening institutional frameworks: This could involve the establishment of independent fiscal agencies or the strengthening of existing institutions responsible for PFM.
- Improving recruitment and training: This could involve the recruitment of skilled personnel and the provision of training and development opportunities to enhance their capabilities.
- Enhancing transparency and accountability: This could involve the publication of financial information and the implementation of measures to prevent corruption and fraud.
- Strengthening monitoring and evaluation: This could involve the establishment of performance indicators and the use of data to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of PFM systems and processes.
To enhance the performance of PFM in Pakistan, several strategies could be adopted, including:
- Strengthening budget preparation and execution: This could involve the implementation of multi-year budgeting and the prioritization of spending on key development areas.
- Improving revenue collection: This could involve the implementation of tax reforms and the introduction of new revenue streams, such as user fees or tolls.
- Enhancing public debt management: This could involve the development of sound debt management policies and the establishment of effective debt management systems.
- Improving financial reporting and auditing: This could involve the enhancement of financial reporting standards and the strengthening of auditing frameworks to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Overall, enhancing the capacity and performance of PFM in Pakistan will require a sustained effort across a range of areas, including institutional strengthening, recruitment and training, transparency and accountability, and monitoring and evaluation.
















































1 thought on “Public Financial Management & General Cadre Bureaucracy in Pakistan”
I totally agree with your words
Kindly send me your all writings .I wanna read !