Amidst the current global challenges, the teachings of the Buddha emphasizing tolerance, compassion, and service to humanity serve as a source of comfort and resilience. As we strive towards a brighter future, let us embrace the essence of Vesak, as expressed by UN Secretary-General António Guterres.
“Vesak,” also known as the Day of the Full Moon in the month of May, holds profound significance as the most sacred day for millions of Buddhists worldwide. It was on the auspicious Day of Vesak, 2,623 years ago, that the Buddha was born, achieved enlightenment, and eventually passed away at the age of eighty.
The United Nations General Assembly, through resolution 54/115 of 1999, formally acknowledges the international observance of the Day of Vesak, recognizing the enduring spiritual contribution of Buddhism, one of the world’s oldest religions. This annual commemoration takes place at the UN Headquarters and other UN offices, in collaboration with relevant UN entities and permanent missions.
The profound teachings of the Buddha, centered on compassion, peace, and goodwill, have deeply resonated with millions of followers worldwide. On the Day of Vesak, adherents honor the birth, enlightenment, and parinirvana of the Buddha, reflecting on his timeless message of compassion and selfless service to humanity.
Former UN Secretary-General Javier Perez de Cuellar, in a message to Buddhists on the Day of Vesak in May 1986, highlighted the significance of celebrating the Buddha’s life and teachings. He emphasized the enduring relevance of the Buddha’s message of compassion and dedication to the betterment of humanity in today’s world, underscoring the importance of peace, understanding, and a global vision that transcends national and international differences.
This philosophy, deeply rooted in the United Nations Charter, remains pivotal in navigating the complexities of the modern age, particularly during the International Year of Peace. It serves as a poignant reminder of the universal values of compassion, peace, and unity that are essential for fostering a harmonious and interconnected global community.
Vesak Day, commemorated by the United Nations, holds significant importance as it acknowledges the contributions of Buddhism to the spiritual and cultural heritage of humanity. The celebration of Vesak at the international level underscores the universal values of peace, compassion, and altruism promoted by Buddhism.
The United Nations’ recognition of Vesak Day provides a platform to highlight the teachings of Buddhism, emphasizing the importance of non-violence, respect for all forms of life, and the pursuit of harmony and understanding among individuals and communities. By commemorating Vesak, the United Nations promotes the principles of tolerance and mutual respect, which are essential for fostering peaceful coexistence in our diverse global society.
Furthermore, Vesak Day serves as a reminder of the shared aspirations for a more peaceful and equitable world. The occasion encourages people of all backgrounds to reflect on the universal truths and ethical principles espoused by Buddhism, such as kindness, generosity, and mindfulness. This global observance reinforces the values of empathy and social responsibility, inspiring individuals to contribute to the well-being of others and work towards the common good.
The United Nations’ recognition of Vesak Day also highlights the role of Buddhism in addressing contemporary challenges, including environmental sustainability, social justice, and conflict resolution. By acknowledging Vesak, the United Nations acknowledges the potential of Buddhist teachings to offer insights and solutions to pressing global issues, contributing to the promotion of a more harmonious and sustainable world.
Therefore, the United Nations’ celebration of Vesak Day underscores the enduring relevance of Buddhist principles in advancing peace, compassion, and sustainable development on a global scale. This recognition serves to foster intercultural dialogue, promote universal values, and inspire individuals and nations to strive for a more peaceful and compassionate world.
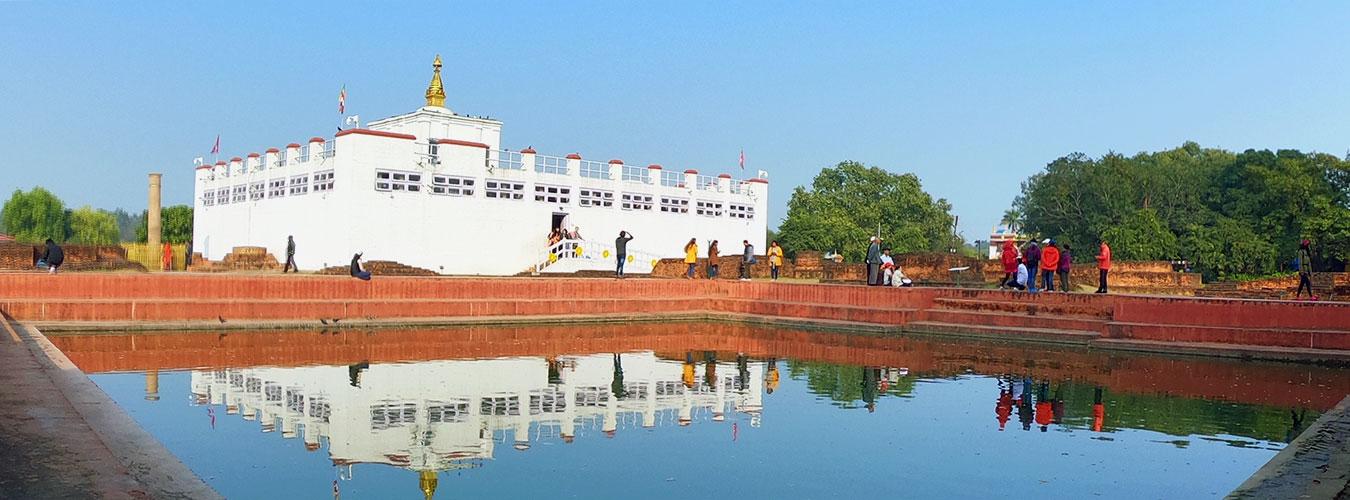
UNESCO is currently working on a project aimed at creating a unique Buddhist Heritage Route for Sustainable Tourism Development in South Asia, with the generous support of the Korea International Cooperation Agency (KOICA). South Asia boasts a wealth of Buddhist heritage, as evidenced by the presence of World Heritage properties throughout the region.
One of the remarkable sites in this heritage is the Borobudur Temple Compounds in Indonesia. This temple complex holds great historical and religious significance, representing the rich cultural heritage of Buddhism in the region. It stands as a testament to the profound influence of religious movements and traditions on the historical Silk Roads, which were crucial trade routes connecting different regions. Notably, Buddhism played a significant role in the development of these trade networks, originating in the Indian Subcontinent and spreading to other areas along the Silk Roads. The Buddhist principles were supportive of trade and commerce, fostering an environment conducive to economic exchange and investment.
The initiative to develop a Buddhist Heritage Route for Sustainable Tourism Development in South Asia underscores the importance of preserving and promoting the region’s rich Buddhist heritage. Through this project, UNESCO and KOICA aim to create a platform for sustainable tourism that not only conserves these culturally significant sites but also provides economic opportunities for local communities. By leveraging the historical and cultural importance of Buddhist heritage, the project seeks to encourage responsible and sustainable tourism practices that benefit both the preservation of these sites and the well-being of the local populations.
The development of this heritage route also aligns with the broader goals of promoting cultural exchange and understanding. By highlighting the historical and spiritual significance of these Buddhist sites, the project aims to foster greater appreciation and awareness of South Asia’s diverse cultural heritage. Furthermore, it seeks to facilitate cross-border cooperation and collaboration among South Asian countries, promoting regional integration and mutual understanding through the shared legacy of Buddhism.
In conclusion, the project to establish a Buddhist Heritage Route for Sustainable Tourism Development in South Asia represents a significant step towards preserving and leveraging the region’s rich Buddhist heritage. By recognizing the cultural and economic potential of these sites, UNESCO and KOICA are working to create sustainable tourism opportunities that benefit both the preservation of heritage and the well-being of local communities while also promoting cultural exchange and regional cooperation.