Abdul Rauf
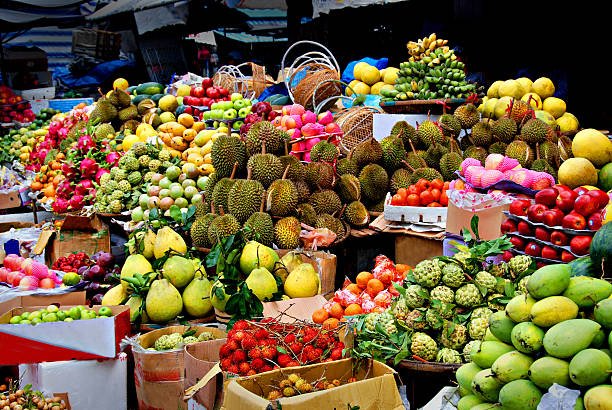
Fruit production is an essential sector of the economy in the modern world, as it provides food, income, employment, and foreign exchange for many countries. Fruits are also rich in nutrients, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, which have various health benefits for consumers. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization Statistics (FAOSTAT), the global fruit production was 1,007.7 million metric tons in 2020.
Pakistan is one of the major fruit-producing countries in the world, with a total fruit production of 11.13 million metric tons in 2021. The major fruit-producing areas of Pakistan are:
Punjab: The largest province of Pakistan, which produces about 60% of the total fruit production in the country. The main fruits grown in Punjab are citrus, mango, guava, apple, peach, plum, apricot, and grapes.
Sindh: The second largest province of Pakistan, which produces about 28% of the total fruit production in the country. The main fruits grown in Sindh are mango, banana, date, guava, and chiku.
Balochistan: The largest but least populated province of Pakistan, which produces about 10% of the total fruit production in the country. The main fruits grown in Balochistan are apples, apricots, cherries, almonds, and pistachios.
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: The northern province of Pakistan, which produces about 2% of the total fruit production in the country. The main fruits grown in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa are apple, peach, plum, pear, and walnut.
Gilgit-Baltistan: The northernmost region of Pakistan, which produces about 0.5% of the total fruit production in the country. The main fruits grown in Gilgit-Baltistan are apricot, cherry, mulberry, and walnut.
The significance of fruit production for Pakistan is evident from the fact that it contributes about 4.5% to the agricultural GDP and 0.8% to the national GDP. It also provides livelihood to about 6 million farmers and employs about 12 million people in the fruit value chain. Moreover, it earns about $460 million from fruit exports, mainly from citrus, mango, and dates. However, fruit production in Pakistan faces many challenges. The changing patterns of temperature, rainfall, and seasons have adverse impacts on fruit crops, such as reduced yield, increased pest and disease incidence, and altered fruit quality and shelf life. The fruit crops are attacked by various pests and diseases, such as fruit flies, mealy bugs, scale insects, aphids, mites, nematodes, fungi, bacteria, and viruses, which cause significant losses in the quantity and quality of the fruits.
Low prices, high intermediation, poor infrastructure, lack of standardization, and weak linkages between the producers and the consumers characterize the fruit market in Pakistan. This results in low profitability, high wastage, and low competitiveness in the fruit sector.
Poor road conditions, inadequate cold storage facilities, and high transportation costs hamper the transportation of fruits in Pakistan. This affects the freshness, quality, and shelf life of the fruits and reduces their market value. Various factors, such as supply and demand, seasonality, quality, variety, and market location, influence the price mechanism of fruits in Pakistan. However, the price mechanism is often distorted by the role of middlemen, who manipulate the prices to their advantage and exploit the farmers and the consumers.
Therefore, it is critical to increase the productivity of fruit production in Pakistan. There are a number of steps that can be taken to increase fruit productivity in Pakistan. Some of the recommendations are to adopt climate-smart agriculture practices, such as using drought-tolerant and pest-resistant varieties, applying water-efficient irrigation methods, and adopting integrated pest-management techniques. Furthermore, improving the post-harvest management of fruits, such as using proper harvesting, grading, packing, and storing methods and applying value-added processing techniques, such as drying, canning, juicing, and jamming, is also significant. It is also vital to enhance the market access and competitiveness of fruits, such as developing market information systems, establishing quality standards and certification schemes, and promoting branding and marketing strategies.
Furthermore, strengthening the transportation and logistics of fruits, such as improving the road network, expanding the cold chain infrastructure, and reducing transportation costs and time, is vital. Accordingly, it is also crucial to reform the price mechanism of fruits, such as eliminating the role of intermediaries, establishing farmer cooperatives and associations, and creating direct linkages between the producers and the consumers. Then there are also administrative recommendations for the production of fruit in Pakistan. The government, administration, and agriculture departments of the provinces need to support the farmers in growing fruit. Farming in Pakistan should be modernized and cover all aspects of crops, including vegetables and fruit.
Accordingly, awareness, administrative support, and farmers’ interest in fruit production in Pakistan are some of the factors that affect the development and growth of the fruit sector in the country. Fruit producers and consumers’ awareness of the importance, benefits, and challenges of fruit production is essential for the promotion and improvement of the fruit sector. However, the awareness level of the fruit stakeholders in Pakistan is low due to the lack of education, training, extension, and communication services. The fruit producers are not aware of the best practices, technologies, and opportunities for fruit production, such as climate-smart agriculture, post-harvest management, value addition, and market access. Fruit consumers need to be made aware of the nutritional, health, and economic value of fruits, and their preferences and demands are influenced by the price, quality, and availability of fruits. Therefore, there is a need to increase the awareness of the fruit stakeholders in Pakistan by providing them with adequate and relevant information, knowledge, and skills through various channels and platforms, such as media, social networks, workshops, seminars, and exhibitions.
Please, subscribe to the monthly magazines of republicpoliyc.ocm
Furthermore, the administrative support of the government and the private sector for fruit production is vital for the provision and facilitation of policies, regulations, incentives, and services for the fruit sector. However, the administrative support of the fruit stakeholders in Pakistan is weak due to the lack of political will, institutional capacity, and coordination among the government and private sector’s different levels and departments. The fruit policies and regulations need to be more consistent, comprehensive, and conducive for the fruit sector, and their implementation and enforcement need to be more effective and efficient. The fruit incentives and services, such as subsidies, credit, insurance, infrastructure, and research and development, are not sufficient, accessible, and affordable for the fruit sector. Therefore, there is a need to enhance the administrative support of the fruit stakeholders in Pakistan by developing and implementing sound and sustainable policies, regulations, incentives, and services for the fruit sector and by strengthening the collaboration and partnership among the government and the private sector.
Finally, the farmer’s interest in fruit production is crucial for the motivation and participation of the farmers in the fruit sector. However, the farmers’ interest in the fruit producers in Pakistan could be higher due to the low profitability, high risk, and high competition of the fruit sector. The fruit profitability is low due to the low yield, low quality, and low price of the fruits. The fruit risk is high due to the uncertainty and variability of the climate, pests, diseases, and markets. The fruit competition is high due to the influx and dominance of imported and processed fruits. Therefore, there is a need to increase the farmer’s interest in fruit producers in Pakistan by improving profitability, reducing the risk, and enhancing the competitiveness of the fruit sector, and by creating and supporting farmer organizations and associations, such as cooperatives, federations, and councils.
Please, subscribe to the YouTube channel of republicpolicy.com